Introduction
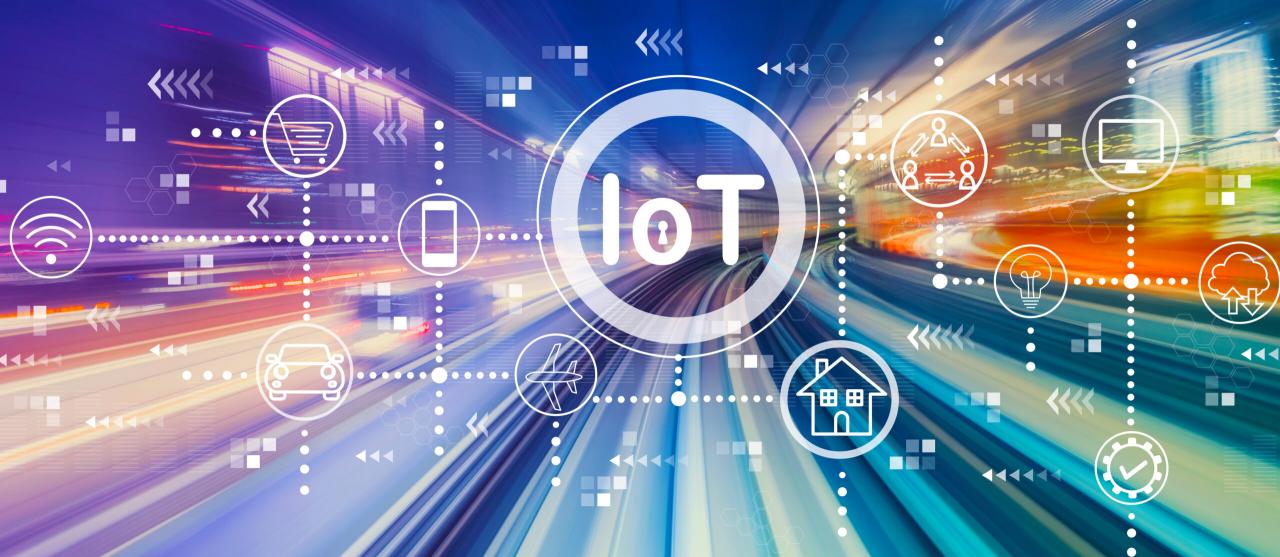
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, connecting devices and systems in unprecedented ways. This article explores the concept of IoT, its current applications, and the potential it holds for the future. With real-world examples and cutting-edge technologies, we delve into the opportunities and challenges presented by the IoT.
Understanding the Internet of Things
Defining IoT and its Components
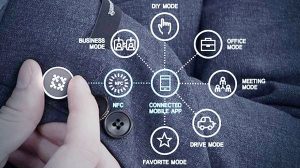
The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data. These objects can range from everyday devices like smartphones and wearable fitness trackers to industrial machinery and smart home appliances. The data collected by these devices provides valuable insights and enables automation, optimization, and improved decision-making.
Key Technologies Powering IoT
Several technologies are at the core of the IoT ecosystem. These include:
- Wireless Connectivity: IoT devices utilize various wireless connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and cellular networks, to transmit data and communicate with each other.
- Sensors: Sensors embedded in IoT devices gather data on various environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, motion, and light. This data is then used for analysis and decision-making.
- Cloud Computing: The massive volume of data generated by IoT devices is stored and processed in cloud computing platforms. Cloud infrastructure provides the scalability and processing power necessary for IoT applications.
- Data Analytics: Advanced analytics techniques, including machine learning and artificial intelligence, analyze the vast amount of data collected from IoT devices. This analysis enables real-time insights, predictive capabilities, and intelligent automation.
Current Applications of IoT
Smart Home Automation
Smart home devices, such as voice assistants, thermostats, security systems, and lighting controls, have become increasingly popular. These devices are interconnected through IoT technology, allowing homeowners to control and automate various aspects of their homes remotely. For example, Amazon’s Alexa can integrate with smart devices, enabling voice-activated control of lights, appliances, and even door locks.
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applies IoT technology to industrial settings, improving operational efficiency and productivity. In manufacturing, connected machines can provide real-time data on equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance and reducing downtime. General Electric’s Predix platform is an example of IIoT implementation, offering analytics and optimization solutions for industrial operations.
Smart Cities
Cities are leveraging IoT to enhance sustainability, efficiency, and quality of life for residents. Smart city initiatives involve using IoT devices and sensors to collect data on traffic patterns, energy usage, waste management, and public safety. Barcelona’s “Smart City” project integrates IoT technology to monitor and optimize energy consumption, parking availability, and transportation systems.
The Future of IoT
Connected Healthcare
IoT has significant potential in healthcare, enabling remote patient monitoring, personalized medicine, and improved healthcare delivery. Connected devices, such as wearables and implantable sensors, can gather real-time health data and transmit it to healthcare providers. This allows for early detection of health issues, proactive intervention, and optimized treatment plans.
Autonomous Vehicles
The IoT plays a vital role in the development of autonomous vehicles. Connected cars rely on sensors and data exchange to navigate, avoid collisions, and optimize traffic flow. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication enable coordination between vehicles and traffic systems, enhancing safety and efficiency on the roads.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Privacy and Security
As more devices are connected, data privacy and security become paramount concerns. Protecting sensitive user information and ensuring the integrity of data transmission are critical. Stricter regulations, robust encryption, and authentication mechanisms are necessary to mitigate risks and build trust in IoT systems.
Interoperability and Standardization
Interoperability among different IoT devices and platforms remains a challenge. Ensuring seamless communication and integration across devices from different manufacturers requires standardized protocols and interfaces. Industry alliances and organizations are working towards establishing interoperability standards to unlock the full potential of IoT.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things presents a world of endless possibilities, transforming industries, cities, and daily life. As Eric Schmidt, former CEO of Google, noted, “The Internet of Things will augment your brain.” By harnessing the power of IoT technologies, we can create a connected future where data-driven insights and automation improve efficiency, sustainability, and quality of life. However, addressing challenges such as data privacy, interoperability, and security is crucial to realizing the full potential of IoT and ensuring its widespread adoption.